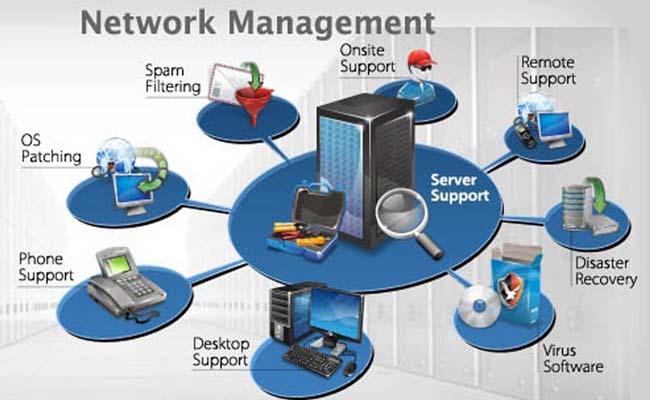
What Is An NMS? And What Is The Purpose Of NMS? A network management system (NMS) is an application or set of applications that lets network engineers manage a network’s independent components inside a bigger network management framework and performs several key functions.
Get more details about Network Management Services.
An NMS identifies, configures, monitors, updates, and troubleshoots network devices both wired and wireless — in an enterprise network.
What Is An NMS? And What Is The Purpose Of NMS?
What Is A Network Management System?
A system management control application then displays the performance data collected from each network component, allowing network engineers to make changes as needed.
Network management is the process of administering, managing, and operating a data network, using a network management system. Modern network management systems use software and hardware to constantly collect and analyze data and push out configuration changes for improving performance, reliability, and security.
Network element vendors make their performance data available to NMS software either through APIs or through a protocol such as NetFlow, a de facto industry standard originally developed by Cisco that allows NetFlow-enabled routers to transmit traffic and performance information.
Network engineers use a network management system to handle a variety of operations, among them:
Variety Of Operations
Monitor performance:
By collecting operating metrics through a series of physical taps, software agents, or Simple Network Management Protocol interfaces, an NMS can provide the visibility necessary to determine if network elements are operating correctly.
Detect devices:
A network management system is used to detect devices on the network and to ensure the devices are recognized and configured correctly.
Analyze performance:
An NMS is used to track performance data indicators, including bandwidth utilization, packet loss, latency, availability, and uptime of routers, switches, and other network components.
Enable notifications:
In the event of a system disruption, an NMS will proactively alert administrators about any performance issues.
How Does A Network Management System Do Its Job?
The system manages network devices such as switches, routers, access points, and wireless controllers. It typically uses a centralized server to collect data from network elements. The server can be located on-premises, in a private data center, or in the cloud.
Devices, clients, and applications on the network can send data to the server with updates about their status. Network administrators can monitor network operations by logging in to the server, usually through a web browser or a smartphone app.
How Do Network Elements Send Data To The System?
Networking devices, such as routers and switches, and network endpoints, such as computers, smartphones, cameras, machines, and sensors, typically send data to the system in one of two ways:
SNMP:
The Simple Network Management Protocol is an open standard and has been the de facto network management protocol since the early 1990s. It is widely supported by most manufacturers of network elements. The network management system uses SNMP to “poll” each element in the network. Each element then sends a response to the system.
Telemetry:
A software agent installed in a network element allows for the automatic transmission of key performance indicators in real-time. Telemetry is rapidly replacing SNMP, because it is more efficient, can produce many more data points,
and is more scalable. And telemetry standards, such as NETCONF/YANG, are gaining traction as ways to offer the same multivendor support as SNMP.